Image Processing
Satellite Imagery is an increasingly powerful tool for mapping and visualizing the world. No other method of imagery acquisition encompasses as much area in as little time.
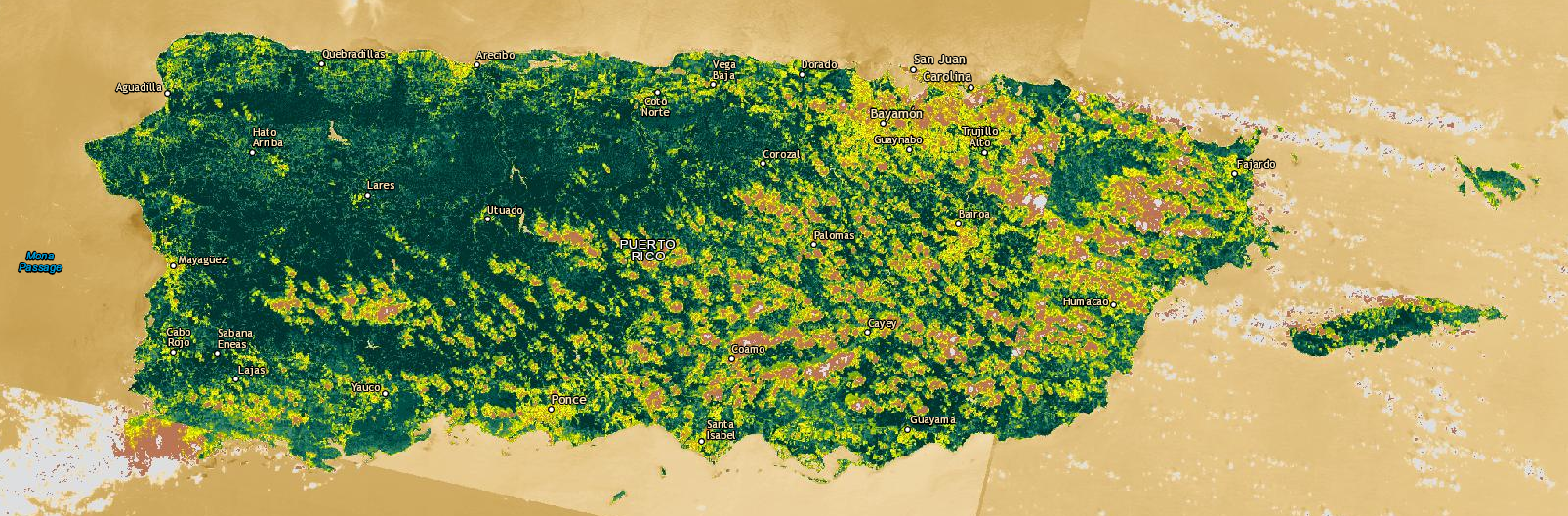
Data Source: U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA).
Imagery expands your perspective
Advantages and Capabilities
Visible Intelligence
- Daily access to new information
- Looking back in time
- Richer data collections
- Powerful analytic capabilities
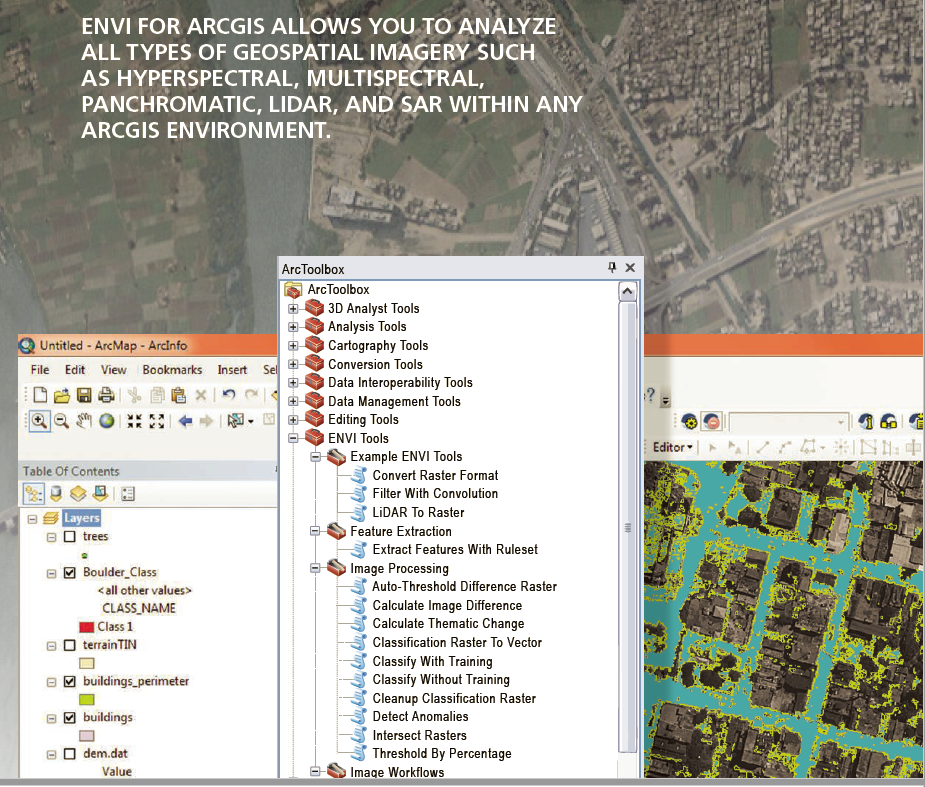
GIS + Imagery
Rasters provide a host of useful GIS data layers.
- Classified land cover and land use
- Distance to water
- Three-dimensional scenes
- Elevation expressed as shaded relief
- Oblique perspective photos
- Time series information
Application Trends
Remote Sensing Industries
- Precision agriculture
- Humanitarian aid
- Forestry
- Mining
- Natural disaster assessment
- Climate and weather study
- Engineering and construction
- Oil and gas
- Urban planning
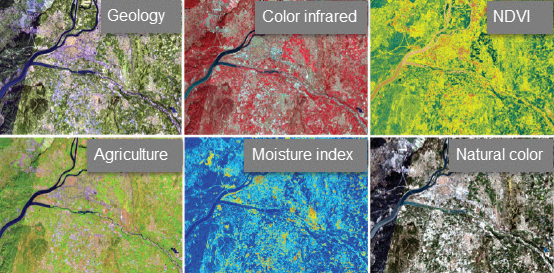
Multispectral imagery can be processed and represented for many purposes, each served directly from the sensor platform on the fly. Image processing algorithms can be applied to the raw imagery in order to represent the results you want to work with. In this example, Landsat 8 scenes are interpreted and simultaneously delivered as real-time image intelligence.
Exploring the Invisible World
Satellite imagery sees things on the electromagnetic spectrum, including what's invisible to the human eye.
Different spectral bands yield insight about our precious and continually changing earth.

Different spectral bands yield insight about our precious and continually changing earth. Scientists and GIS analysts use Landsat to keep an eye on places like the Cambridge Gulf in Australia (above), where mangroves are threatened by cyclones and industrialization.